Industrial wastewater treatment is a major challenge for sectors such as textiles, paper, and metal processing. These industries generate large volumes of wastewater containing dyes, suspended solids, heavy metals, and other harmful pollutants. To meet environmental regulations and reduce ecological impact, companies need treatment solutions that are both effective and economical.
Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC) has become a key chemical in industrial wastewater treatment. It offers better flocculation, faster sedimentation, and improved overall treatment efficiency compared to many traditional coagulants.
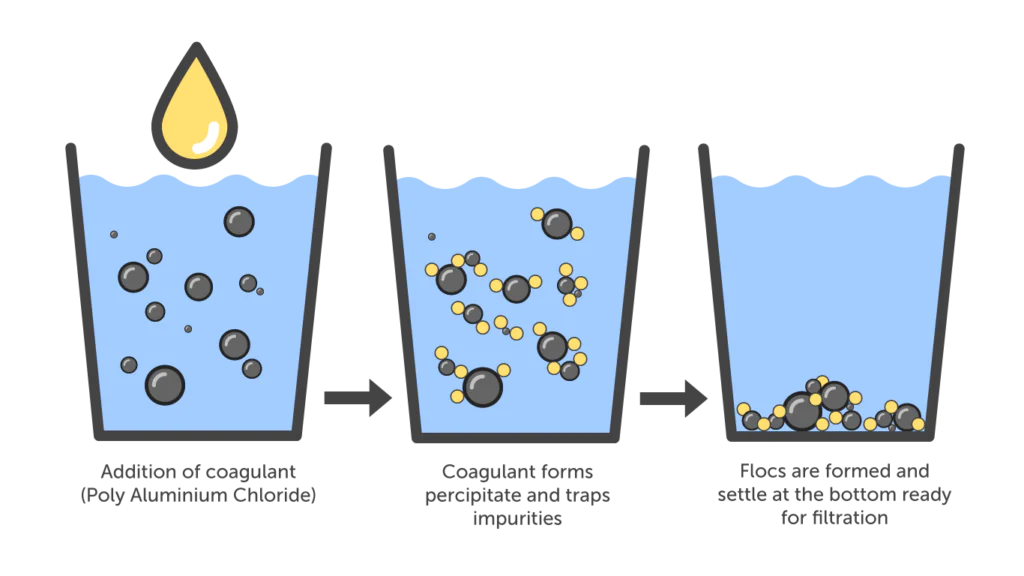
The Challenge of Industrial Wastewater
Industrial wastewater often contains complex contaminants that are difficult to remove. Traditional coagulants like alum and ferric chloride have been widely used, but they come with several drawbacks:
- High sludge production
- Performance affected by pH changes
- Higher overall chemical consumption
These limitations increase operational costs and make treatment less efficient, especially for industries with high wastewater volumes.
PAC’s Role in Industrial Wastewater Treatment
PAC is increasingly used as an alternative to conventional coagulants. Its highly charged polymer structure helps destabilize fine particles and promotes strong coagulation and flocculation.
One of PAC’s main advantages is the formation of larger and stronger flocs. These flocs are easier to remove through sedimentation or filtration. This is especially useful in industries like textile and paper production, where wastewater contains large amounts of color, fibers, and suspended solids.
Faster Sedimentation for Higher Treatment Capacity
PAC not only improves floc formation but also increases sedimentation rates. Faster settling of solids shortens treatment time and improves plant throughput.
For industries with continuous and high-volume wastewater discharge, such as metal processing plants, this means more wastewater can be treated without expanding infrastructure. Faster clarification also helps maintain stable treatment performance.

Cost Efficiency and Operational Advantages
Switching to PAC can lead to noticeable cost savings. Because PAC works efficiently at lower dosages, chemical consumption can be reduced. In addition, PAC produces less sludge, which lowers sludge handling and disposal costs.
Another benefit is PAC’s ability to work effectively across a wider pH range. This reduces the need for frequent pH adjustment chemicals, simplifying operations and cutting additional expenses.
Overall, PAC helps plants:
- Lower chemical costs
- Reduce sludge volume
- Improve treatment stability
- Simplify process control
Real-World Results: PAC in Industrial Applications
Many industries have reported improved performance after adopting PAC. For example, textile plants have achieved lower chemical use and reduced sludge generation. Paper mills have seen faster flocculation and improved sedimentation, allowing higher daily treatment capacity without raising operating costs.
These results show how PAC supports both environmental compliance and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC) is a reliable and cost-effective choice for industrial wastewater treatment. Its ability to enhance flocculation, speed up sedimentation, and reduce sludge makes it especially valuable for industries with large and complex wastewater streams.
As environmental standards become stricter, PAC offers a practical solution for companies aiming to improve efficiency, lower costs, and maintain regulatory compliance.
