Water treatment relies heavily on coagulation and flocculation to remove suspended solids, organic matter, and turbidity. While chemicals like alum and ferric salts are the main coagulants, calcium chloride (CaCl₂) plays an important supporting role as a coagulation aid.
It helps improve floc formation, enhance settling, and increase overall treatment efficiency.
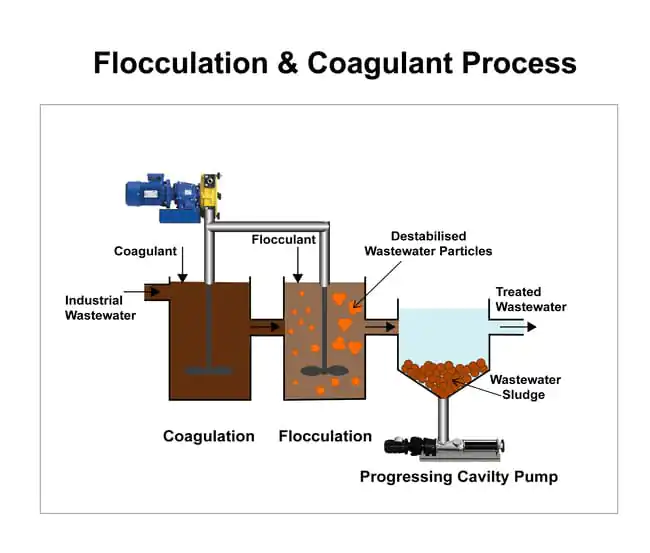
What Are Coagulation and Flocculation?
Coagulation is the process of adding a chemical that destabilizes fine particles in water. Most particles carry negative charges and stay suspended. Coagulants neutralize these charges so particles can come together.
Flocculation follows coagulation. Gentle mixing allows small particles (microflocs) to combine into larger flocs that can settle or be filtered out.
The Role of Calcium Chloride in Water Treatment
Calcium chloride is not usually the primary coagulant. Instead, it works as a treatment enhancer by improving water chemistry conditions that favor coagulation and flocculation.
When dissolved in water:
The released calcium ions (Ca²⁺) support the treatment process in several ways.
How Calcium Chloride Supports Coagulation
1️⃣ Improves Particle Destabilization
Natural water often contains organic matter and fine colloids that are difficult to remove. Calcium ions help reduce repulsion between particles, making it easier for primary coagulants (like alum or ferric chloride) to work effectively.
This leads to faster and stronger microfloc formation.
2️⃣ Increases Water Hardness and Ionic Strength
Higher ionic strength compresses the electrical double layer around particles. This reduces particle stability and allows them to collide and stick together more easily during coagulation.
3️⃣ Supports Alkalinity Balance
Some coagulants consume alkalinity and lower pH. Calcium chloride can help stabilize water chemistry in certain systems, especially when used together with lime or alkalinity adjustment chemicals.
Stable pH improves coagulant performance.
How Calcium Chloride Enhances Flocculation
During flocculation, calcium ions help strengthen the structure of growing flocs.
✔ Stronger Floc Formation
Calcium can form bridges between particles and organic matter, making flocs denser and more stable.
✔ Faster Settling
Heavier, stronger flocs settle more quickly in sedimentation tanks.
✔ Better Filtration
Well-formed flocs are easier to remove in sand or multimedia filters, reducing filter load.

Benefits of Using Calcium Chloride as a Coagulation Aid
Improved Turbidity Removal
Helps achieve lower turbidity after clarification and filtration.
Reduced Coagulant Demand
In some cases, it allows lower doses of primary coagulants, reducing sludge production.
Better Performance in Cold Water
Calcium ions help improve floc formation when low temperatures slow reaction rates.
Wide Compatibility
Works well with:
- Aluminum sulfate (alum)
- Ferric chloride
- Polyaluminum chloride (PAC)
- Organic flocculants (PAM)
Typical Application Areas
Calcium chloride is commonly used in:
- Municipal drinking water treatment
- Industrial wastewater treatment
- Surface water clarification
- High-turbidity water treatment systems
It is especially useful when raw water has low hardness, low ionic strength, or poor floc formation.
Important Application Considerations
Correct Dosage Matters
Overdosing may increase dissolved solids unnecessarily. Jar testing is recommended.
Not a Replacement for Primary Coagulants
Calcium chloride enhances performance but does not replace alum, ferric salts, or PAC.
System Monitoring Required
Operators should monitor turbidity, pH, and settling performance to optimize dosing.
Conclusion
Calcium chloride is a valuable coagulation aid in water treatment. By supplying calcium ions, it improves particle destabilization, strengthens floc structure, and enhances settling and filtration performance.
When used together with primary coagulants and proper process control, calcium chloride helps water treatment plants achieve clearer water, more stable operation, and improved overall efficiency.
