Introduction
The paper making industry, one of the largest manufacturing sectors globally, faces a variety of challenges. Among the most pressing issues are raw material shortages, particularly for paper fibers, and growing environmental concerns. As recycling waste paper becomes a more critical solution, the deterioration of recycled fibers during multiple reuse cycles adds to the problem. The introduction of chemicals like Polyacrylamide (PAM) has emerged as an effective way to address these challenges and improve production efficiency.

What Are the Main Problems in Paper Making?
Paper production, while essential, often involves environmental and operational challenges:
- Resource Scarcity: Many paper mills rely heavily on wood, a resource that has led to deforestation and significant environmental harm.
- Waste Paper Fiber Degradation: Recycled fibers, often used in place of virgin wood, degrade over time. Each cycle of recycling shortens fiber lengths, making the paper weaker and more prone to tearing and breaking.
- Environmental Pollution: The production process produces air and water pollutants, contributing to climate change and water contamination. Chemicals used in pulp processing can also enter water supplies, creating a need for better waste management solutions.

What Is Polyacrylamide (PAM) and How Does It Help?
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a water-soluble polymer that plays a pivotal role in enhancing the performance of paper mills. It helps mitigate the issues faced in the paper-making process by:
- Strengthening Recycled Fibers: PAM can help maintain the integrity of fibers during multiple recycling cycles by enhancing their bonding strength.
- Enhancing Water Efficiency: By improving the retention of fibers and fillers, PAM reduces the need for excessive water usage, which is both an environmental and cost concern.
- Reducing Wastewater Pollution: PAM plays a significant role in improving the treatment of wastewater generated during paper production, reducing harmful effluent discharge into the environment.

PAM’s Key Functions in Paper Making
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is versatile in its application across different stages of paper making, providing a variety of benefits:
- Fiber Retention: PAM helps in improving fiber retention during the papermaking process. By forming stronger bonds between the fibers, it ensures better paper quality, which is especially important when using recycled fibers.
- Paper Strength Enhancement: Cationic PAM is frequently used as a dry strength agent. It helps in enhancing the paper’s wet and dry strength, making it less prone to tearing, even in the recycling process. This is essential for the paper mill’s operational efficiency.
- Filtration Aid: PAM is used as a filter aid, improving the filtration process by making it more efficient. This is crucial in separating water from the pulp slurry, reducing the need for additional water treatment and helping in water reuse.
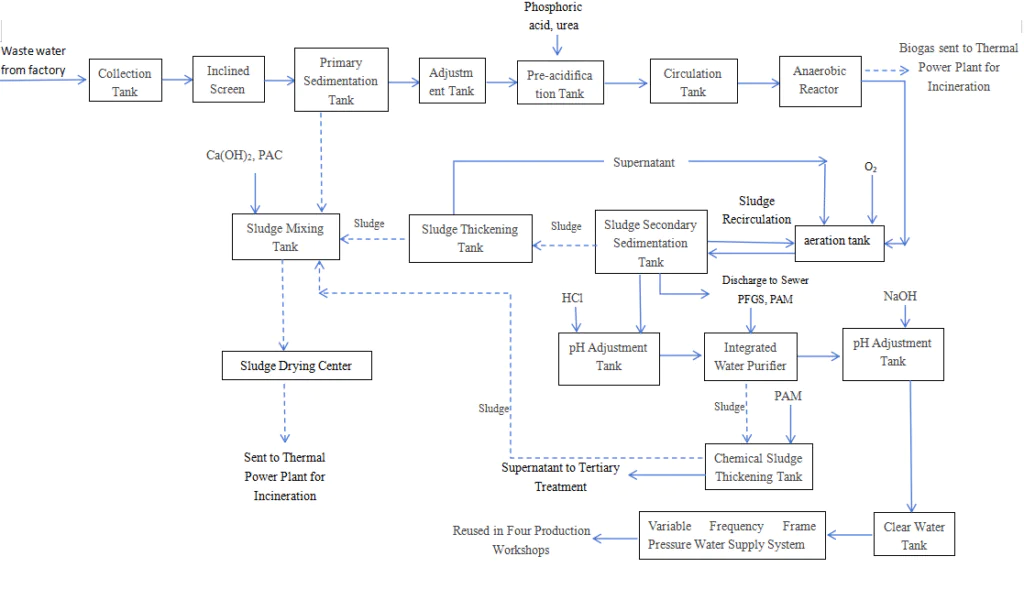
- Water Treatment: Polyacrylamide is an effective agent for wastewater treatment in paper mills. It binds with impurities and particles, making it easier to remove them, which helps meet environmental regulations and promotes sustainability in paper production.
How Does PAM Improve Paper Production Efficiency?
The use of PAM in paper mills results in several operational benefits:
- Reduced Water Usage: By improving fiber retention and reducing waste, PAM helps minimize the water required in the process.
- Improved Fiber Quality: Even with recycled paper, PAM helps maintain the strength of fibers, resulting in higher-quality end products.
- Cost Savings: Reduced water and chemical usage, along with improved fiber retention, can result in lower overall operational costs for paper mills.
Is PAM Environmentally Friendly in the Paper Industry?
While Polyacrylamide (PAM) significantly contributes to improving operational efficiency and quality in paper mills, environmental concerns around its use persist:
- PAM’s Potential Environmental Impact: Acrylamide, a component of PAM, is considered a potential carcinogen, raising concerns about its environmental contamination, particularly through water discharge.
- Wastewater Treatment: However, when used in controlled amounts, PAM can improve the treatment of wastewater, which in turn reduces the environmental impact of paper production. PAM helps to remove harmful particles and pollutants from the effluent, making it easier to meet environmental standards.

Summary
In conclusion, Polyacrylamide (PAM) serves as a versatile and effective solution to many challenges in the paper making industry. From improving fiber retention and paper strength to aiding in water treatment, PAM offers a wide range of benefits that not only enhance the quality and efficiency of paper mills but also contribute to better environmental practices. As such, it plays an essential role in the sustainable development of the paper industry, making it a crucial ingredient for paper manufacturers and chemical suppliers alike.
