Agricultural wastewater treatment has become increasingly important as modern farming, livestock breeding, and agricultural product processing continue to expand. Compared with domestic sewage, agricultural wastewater often contains higher pollutant concentrations and more complex components, making treatment more challenging.
Polyaluminium Chloride (PAC) is widely applied in agricultural wastewater treatment due to its strong flocculation ability, stable performance, and cost-effectiveness.

Characteristics of Agricultural Wastewater
Agricultural wastewater mainly comes from:
- Livestock and poultry breeding
- Aquaculture farms
- Agricultural product processing plants
- Fertilizer and pesticide runoff
Typical characteristics include:
- High COD and chroma
- High phosphorus and ammonia nitrogen
- Suspended solids and colloidal particles
- Poor biodegradability
- Potential toxicity
These factors can cause severe environmental damage if untreated.
Why PAC Is Effective for Agricultural Wastewater
PAC is a high-efficiency inorganic polymer flocculant. During hydrolysis, it forms stable polynuclear aluminum complexes that can:
- Neutralize negative charges on pollutants
- Adsorb suspended solids and colloids
- Promote rapid flocculation and sedimentation
Unlike traditional aluminum salts, PAC works effectively without causing drastic pH changes, which is crucial for process stability.
Removal of Key Pollutants Using PAC
1. COD and Chroma Reduction
PAC aggregates organic pollutants and fine particles, allowing them to settle or be removed through flotation. This significantly reduces COD and improves wastewater appearance.
2. Phosphorus Removal
PAC reacts with phosphate ions to form insoluble aluminum phosphate, enabling effective phosphorus removal.
3. Ammonia Nitrogen Control
Although PAC does not directly oxidize ammonia nitrogen, it:
- Improves solid-liquid separation
- Enhances biodegradability
- Creates favorable conditions for biological treatment
When combined with physical or biological methods, ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency improves significantly.
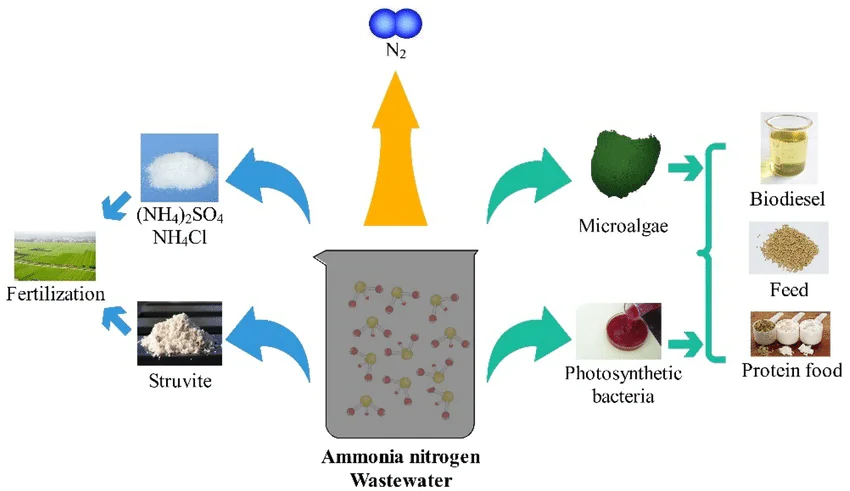
Integration With Other Treatment Technologies
In agricultural wastewater treatment, PAC is often used together with:
- Micro-electrolysis systems for organic degradation
- Biological treatment units
- Advanced filtration processes
PAC acts as a key pretreatment chemical, stabilizing influent quality and protecting downstream systems.
Operational Advantages of Using PAC
PAC offers several practical benefits for agricultural wastewater treatment plants:
- Low dosage and high efficiency
- Easy storage and operation
- Low corrosion to pipelines and equipment
- Reduced sludge volume compared with traditional coagulants
These advantages make PAC suitable for large-scale and decentralized agricultural treatment systems.
Procurement Considerations for Agricultural Applications
When selecting PAC for agricultural wastewater, buyers should focus on:
- Al₂O₃ content and polymerization degree
- Insoluble matter level
- Compatibility with existing treatment processes
- Supplier technical support for jar testing
Choosing the correct PAC grade helps ensure:
- Stable discharge compliance
- Lower long-term operating costs
Conclusion
PAC plays a vital role in agricultural wastewater treatment by effectively removing COD, phosphorus, suspended solids, and improving biodegradability. Its stability, efficiency, and cost advantages make it a mainstream solution for modern agricultural wastewater management.
With proper selection and integration, PAC helps agricultural enterprises meet environmental regulations while protecting surrounding ecosystems.
